2025. 1. 17. 00:57ㆍComputerScience/OperatingSystem
C Standard Library
- In this chapter, let's implement basic types and memory operations, as well as string manipulation functions. In this book, for the purpose of learning, we'll create these from scratch instead of using C standard library.
- The concepts introduced in this chapter are very common in C programming, so ChatGPT would provide solid answers. If you struggle with implementation or understanding any part, feel free to try asking it or ping me.
- 올해 목표 - 코딩할 때 ChatGPT 사용 자제하기 . . ^^.
Basic types
- First, let's define some basic types and convenient macros in common.h
- 우선 기본 타입들과 매크로를 정의한다.
typedef int bool;
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned short uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
typedef unsigned long long uint64_t;
typedef uint32_t size_t;
typedef uint32_t paddr_t;
typedef uint32_t vaddr_t;
#define true 1
#define false 0
#define NULL ((void *) 0)
#define align_up(value, align) __builtin_align_up(value, align)
#define is_aligned(value, align) __builtin_is_aligned(value, align)
#define offsetof(type, member) __builtin_offsetof(type, member)
#define va_list __builtin_va_list
#define va_start __builtin_va_start
#define va_end __builtin_va_end
#define va_arg __builtin_va_arg
void *memset(void *buf, char c, size_t n);
void *memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n);
char *strcpy(char *dst, const char *src);
int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);
void printf(const char *fmt, ...);
Most of these are available in the standard library, but we've added a few useful ones:
- paddr_t: A type representing physical memory addresses.
- vaddr_t: A type representing virtual memory addresses. Equivalent to uintptr_t in the standard library.
- align_up: Rounds up value to the nearest multiple of align. align must be a power of 2.
- is_aligned: Checks if value is a multiple of align. align must be a power of 2.
- offsetof: Returns the offset of a member within a structure (how many bytes from the start of the structure).
align_up and is_aligned are useful when dealing with memory alignment. For example, align_up(0x1234, 0x1000) returns 0x2000. Also, is_aligned(0x2000, 0x1000)returns true, but is_aligned(0x2f00, 0x1000) is false.
The functions starting with __builtin_ used in each macro are Clang-specific extensions (built-in functions).
Memory operations
The memcpy function copies n bytes from src to dst
void *memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n) {
uint8_t *d = (uint8_t *) dst;
const uint8_t *s = (const uint8_t *) src;
while (n--)
*d++ = *s++;
return dst;
}
The memset function fills the first n bytes of buf with c.
This function has already been implemented in Chapter 4 for initializing the bss section.
void *memset(void *buf, char c, size_t n) {
uint8_t *p = (uint8_t *) buf;
while (n--)
*p++ = c;
return buf;
}
String operations
Let's start with strcpy. This function copies the string from src to dst
앞서 구현한 memory copy와 유사하게 이번에는 문자열 버전으로 구현하는 것 !
char *strcpy(char *dst, const char *src) {
char *d = dst;
while (*src)
*d++ = *src++;
*d = '\0';
return dst;
}
* The strcpy function continues copying even if src is longer than the memory area of dst. This can easily lead to. bugs and vulnerabilities (운영체제 시간에 유사한 방식의 해킹(?)사례에 대해 배웠다.!) so it's generally recommended to use alternative functions instead of strcpy. Never use it in production! For simplicity, we'll use strcpy in this book, but if you have the capacity, try implementing and using an alternative function (strcpy_s) instead. - Warning 메세지로도 자주 나왔던 내용!
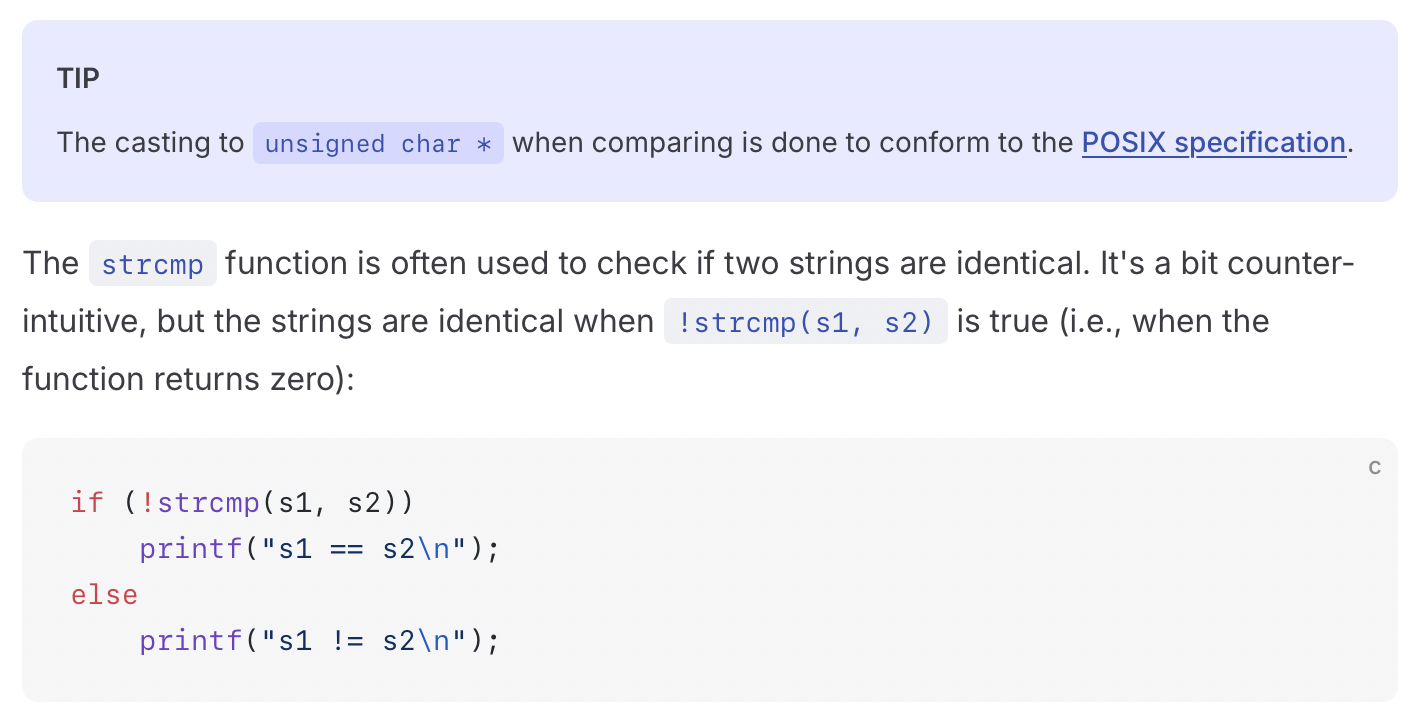
Next function is the strcmp function. It compares s1 and s2 and returns
int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2) {
while (*s1 && *s2) {
if (*s1 != *s2)
break;
s1++;
s2++;
}
return *(unsigned char *)s1 - *(unsigned char *)s2;
}
'ComputerScience > OperatingSystem' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [OS Project] Chap8. Exception (0) | 2025.01.17 |
|---|---|
| [OS Project] Chap7. Kernel Panic (0) | 2025.01.17 |
| [OS Project] Chap5. Hello World! (0) | 2025.01.16 |
| [OS Project] Chap4. Booting the Kernel (0) | 2025.01.13 |
| [OS Project] 운영체제 구현하기 프로젝트 (0) | 2025.01.10 |